(InstaGrap 개발) 코드 채점 프로그램 개발 보고서
by 줌코딩
InstaGraP이란?
인스타그랩은 Instant Programming Assignment Program으로 백준과 프로그래머스와 같은 채점프로그램이다. 이것은 OS에서 배운 Process, Multithread programming, signal, server-client communication 등등을 실제로 구현해볼 수 있는 기회이다. 코드를 제출하는 자(submitter), 코드를 받고 채점거리를 주는 자(Instagrapd), 실제로 코드를 컴파일하고 결과를 확인해주는 자(worker) 을 이용해서 만들었다. ㅎㅎ 아래는 결과 이미지와 보고서이다.
구현 모습
아래 사진들은 구현된 채점 모습이다. UI는 따로 구축하지 않은 점 양해해주길 바랍니당ㅎㅎ
왼쪽이 Worker이고, 중간이 Instagrapd, 오른쪽이 Submitter이다.
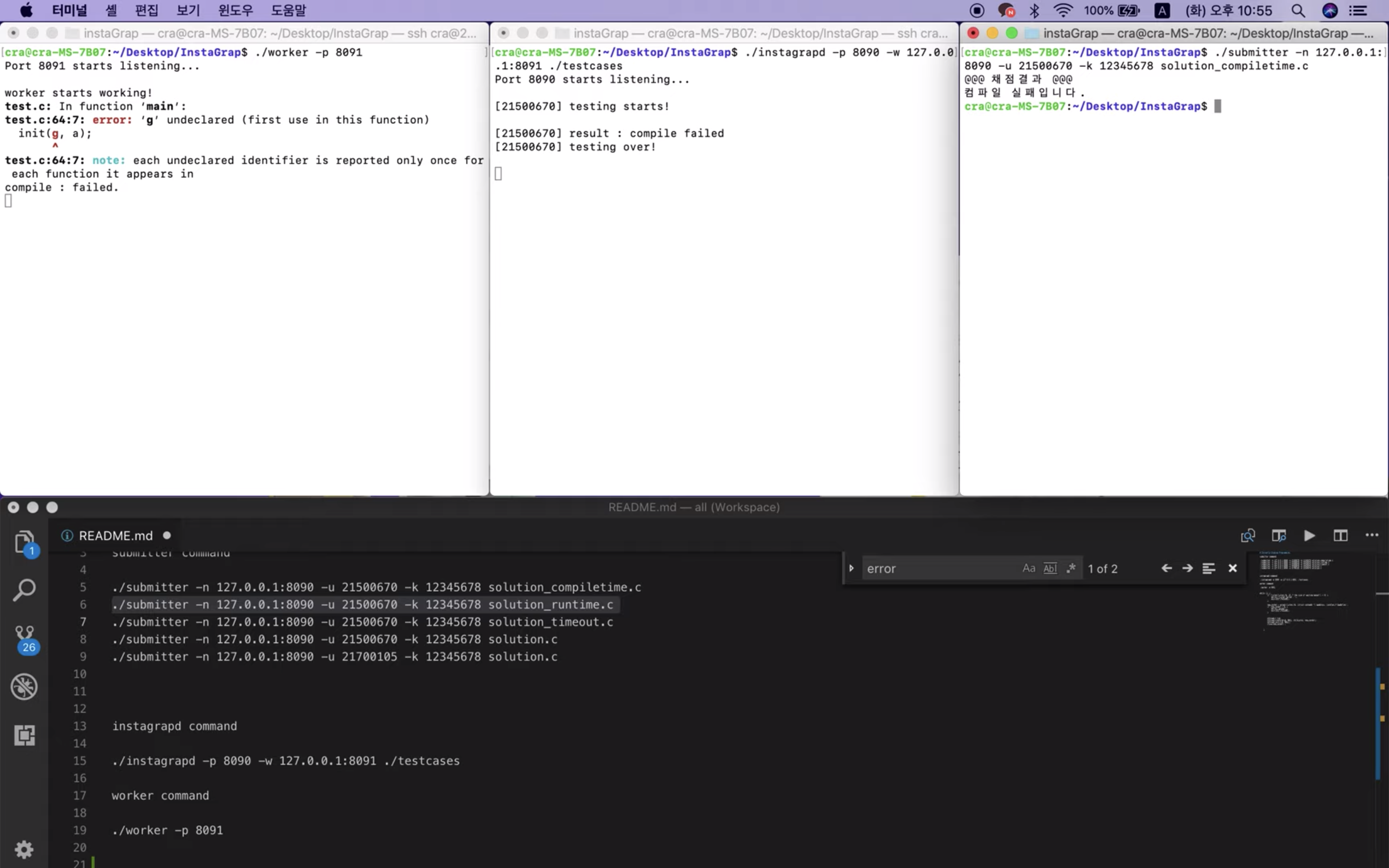
컴파일 에러가 있는 코드 제출 시
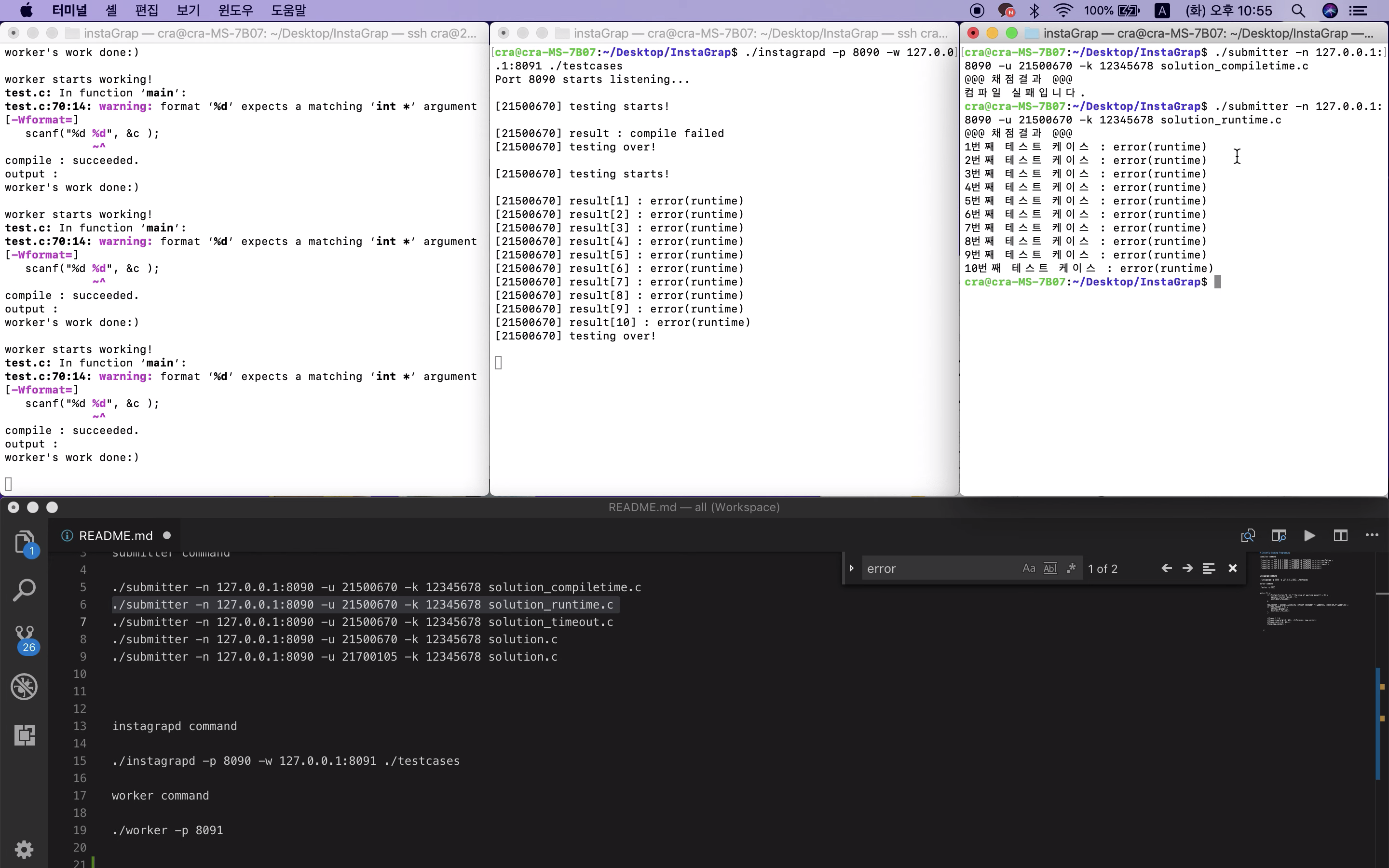
런타임 에러가 있는 코드 제출 시
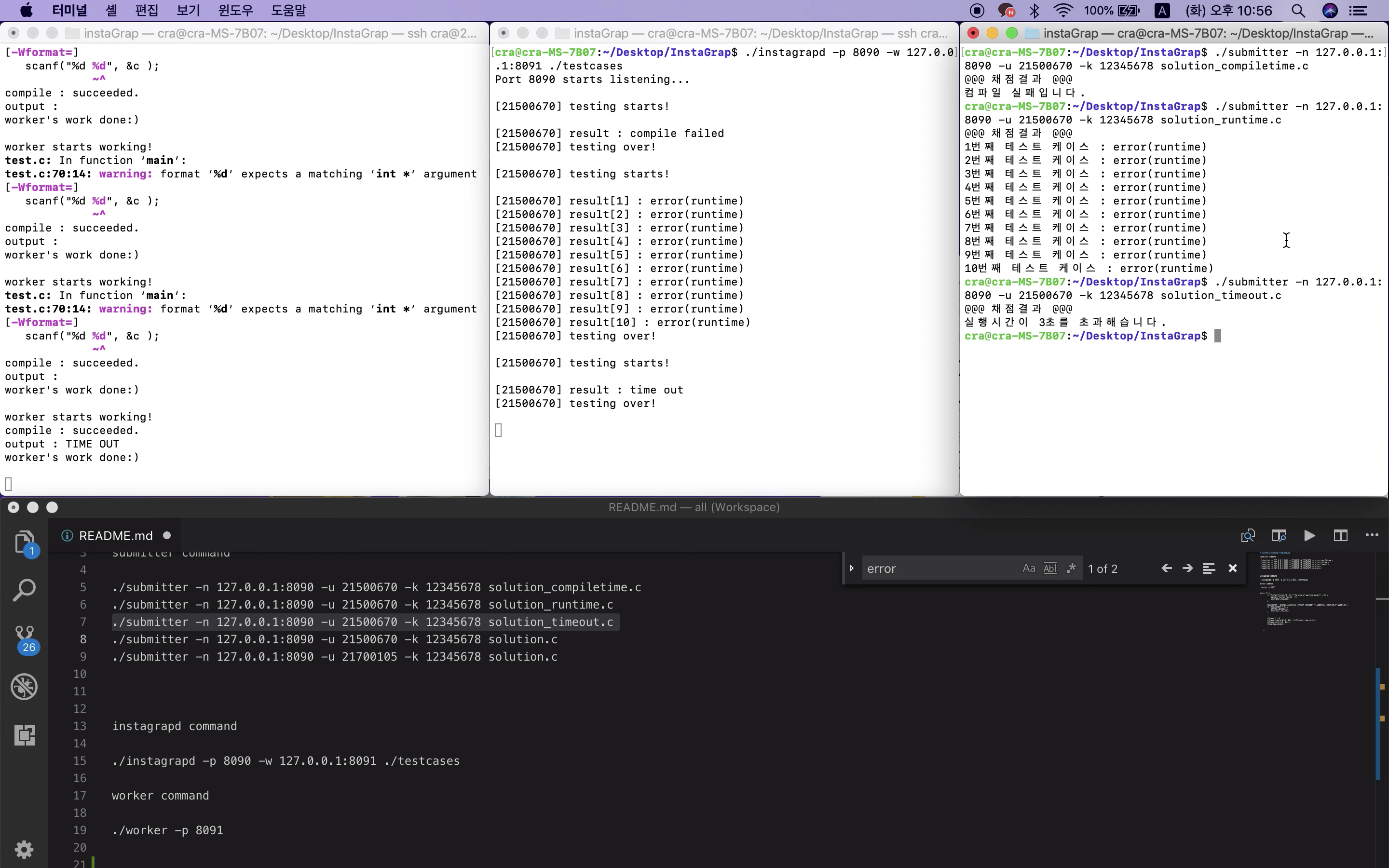
채점 시간(3초) 초과 시
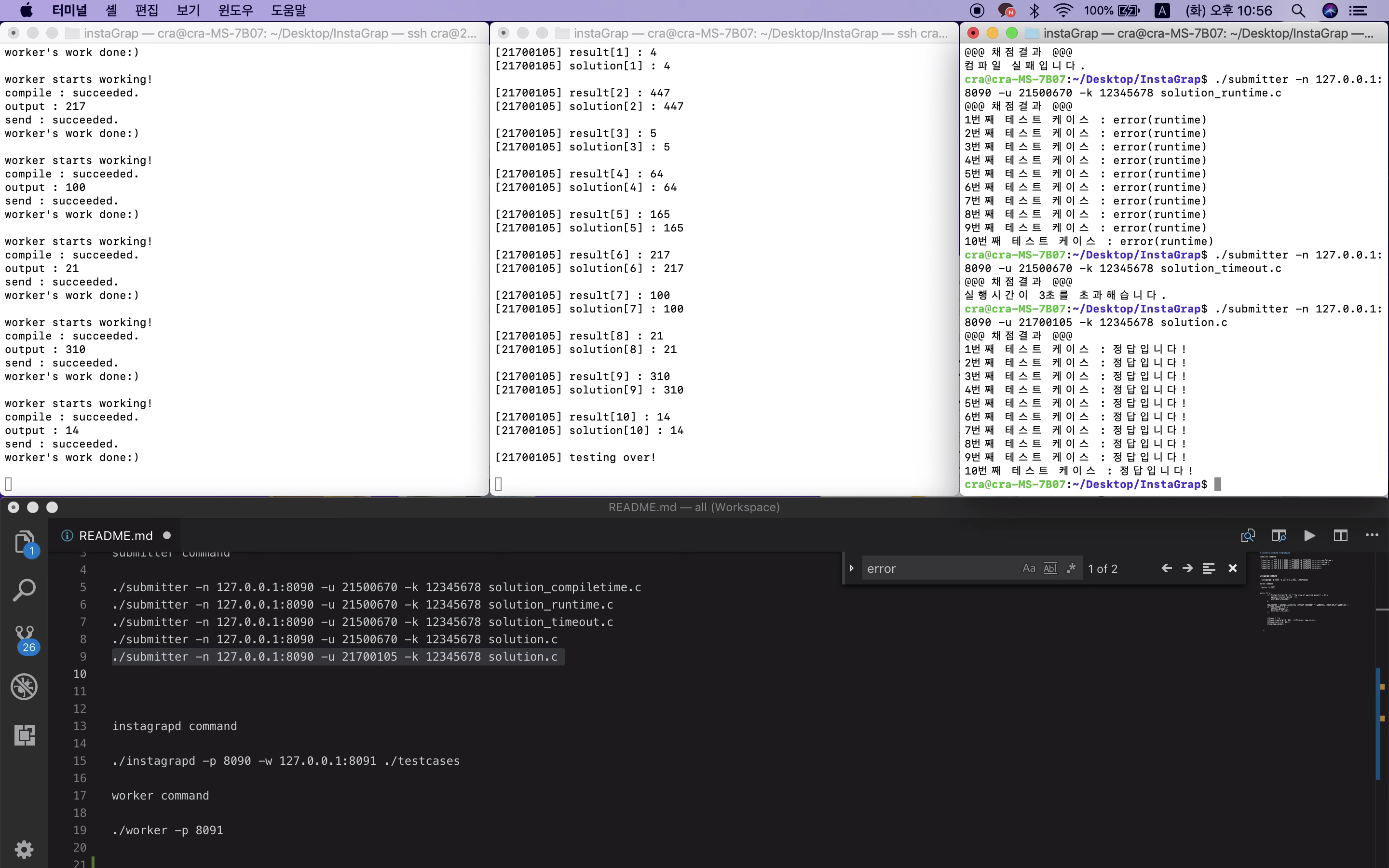
에러 없는 코드 제출 시(해당 코드의 Output도 맞는 경우)
보고서
1. Introduction
1.1 The popularity of the Instant Grading Program
If you are a student majoring in Computer Science(CS), you must have heard about Baekjoon or Programmers. They are very popular among CS students as the understanding of Algorithms and Data Structure has been highly valued by many companies. Basically, what the program does is giving a computer problem with certain inputs and make users to make a solution generating certain outputs.
1.2 Motivation for InstaGrap
As we discussed about intercommunication among processes, multiprocessing and multithreading, developing the instant grading program seems to be a good chance to understand what we have learn by actual implementation.
2. Knowledge needed for InstaGrap
2.1 Process Communication
There are two kinds of communication between processes. One is within the process which is, InterProcess Communication(IPC). When a parent process creates a child process, communication between them might be needed. To enable the interaction, shared memory and message passing are used. There is another kind of communication, which happens in client-server process. This can be done using sockets and pipes. A socket is defined as an endpoint for communication. A communication between a pair of applications consists of a pair of sockets, one at each end of communication channel. Pipes provide a relatively simple ways for processes to communicate with one one another. Ordinary pipes allow communication between parent and child processes, while named pipes permit unrelated processes to communicate.
2.2 Multiprocessing and Multithreading
A process is a program in execution. Operating systems provide a mechanism for one process to create new child processes which enables multiprocessing. The parent process can wait for its children to terminate or parent and child processes can execute concurrently. A thread is a flow of control within a process. A multithreaded process can have several different flows of control within a single process. Using multiple threads, the program can have multiple benefits such as increased responsiveness to the user, resource sharing within the process, economy, and scalability factors. By utilizing multiple threads and processes, a program can have many benefits. However, there can be some issues asides from the benefits. It is important to schedule the processes and threads well and make their memory access correct.
2.3 Standard I/O
These are standard streams for input, output, and error output. By default, standard input is read from the keyboard, while standard output and standard error are printed to the screen. To be more precise, stdin, stdout, and stderr are stream pointers available to access the standard streams. These pointers can be used as argument to functions. Typical examples are getchar and putchar. They use stdin and stdout respectively.
3. InstaGrap Implementation
3.1 The Program Overview
This program is to grade a given C file from the user(submitter). When a user gives a C file and user information, the administrator(instagrapd) starts grading with various inputs. The administrator gives tasks to worker to do execution of the code and receives the result from the worker. When the grading is all over, the submitter receives the result.
3.2 Communication Between Processes
There needs to have communication between processes. As each Processes are in remoted places, the communication should not be made by files or IPC methods. For each communication, TCP socket communication. Even though it is slower than the UDP communication, it is more reliable to use TCP socket communication as it checks the connection is successfully made.
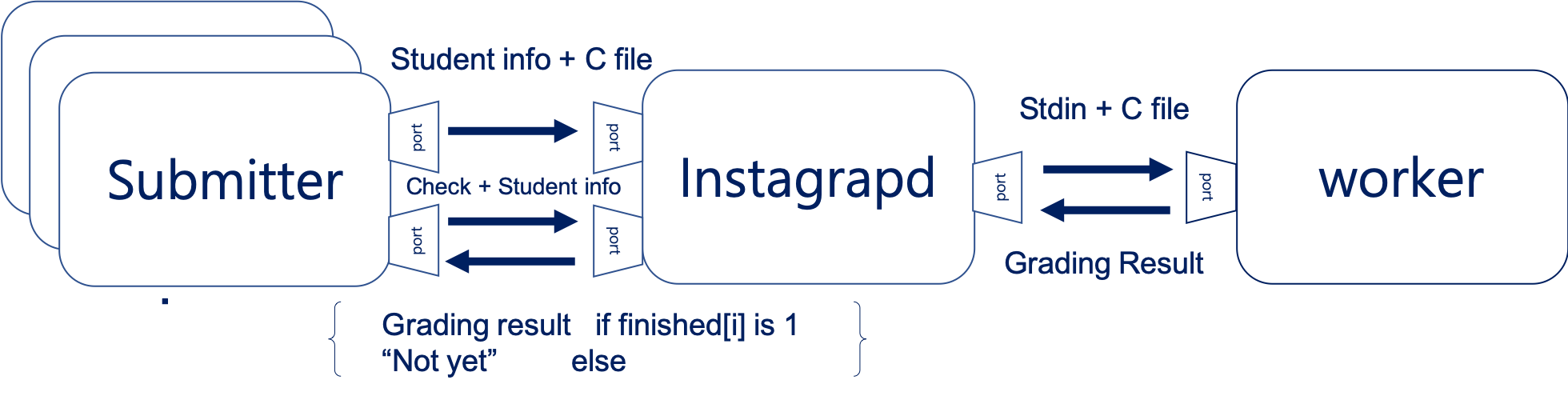
Fig 1. The Overall Communication among Processes
However, the cost for the communication is highly expensive for the socket communication. This is because the socket continues to sit and wait for messages to come. Therefore, this program repeats creating and closing the connection between the processes.
3.2.1 between submitter and instagrapd
For the communication between submitter and instagrapd, there are two communications. The first is for giving the student information(the student ID and the password) and the target c file. Once the connection is made and message is successfully delivered, the connection is closed without waiting. The second communication is for checking the result is ready. By giving the student ID and the password, submitter frequently communicate with instagrapd to check whether the result is ready or not. When instagrapd receives the information, it checks whether the grading is done by using check_user_table().(This will be explained in the latter part.) If the grading result is ready, it returns the results to submitter. Otherwise, it tells submitter to wait and close the connection again.
3.2.2 between instagrapd and worker
The communication between instagrapd and worker is made with sockets either. instagrapd sends the code and one standard input(stdin). After worker finishes grading, it returns the grading result back to the instagrapd and closes the connection.
3.2.3 How to send the multiple data in TCP
To send data to each to one another with multiple data, the data has been put into one single string (char*) and used ‘@’ to indicate where to trim. When the data is get to each process, the data is parsed using strtok().
3.3 Inside submitter
submitter receives the data by the arguments. First, it sends the code and the student information to instagrapd. After then, it frequently creates the connection with instagrapd and receives the result back and print.
3.4 Inside instagrapd
When it is started, it creates a port for the submitters to connect. As the connection is made, it creates a child process to handle the communication within the connection and goes back to the listening. When thecode is received from submitter, it makes a connection to worker. Then, it gives worker a stdin file and the code for 10 times. Whenever, submitter makes a connection to instagrapd, it checks the user table to see whether the grading result is ready.
3.4.1 How to store the grading result from worker
As it has to send the code and receive the grading results from worker for the amount of testcases, instagrapd should store the grading result to somewhere. For this, a file named by the student ID is created. and continuously the grading result is accumulated.
3.4.2 Handling Multiple Users
There are global variables to handle multiple users. In instagrapd, arrays for id, password, and finished exist. The array named finished contains information about whether the result is ready or not. When the student information is given, the data is put to empty space for id and pw array.
int id[100]; char pw[100][20]; int finished[100];
As submitter’s request received, it checks whether the ID and the password exist and are correct by check_user_table(). If it is correct, it gets the index according to the id and see finished[index]’s value. If it is 1, the id, pw, finished for the index are all initialized, and returns the accumulated grading result back to submitter. If it is 0, it sends submitter “wait.”
3.5 Inside worker
worker is to compile and run the given source code with the standard input and returns the result to instagrapd. The parent process create child process and run in a synchronous manner.
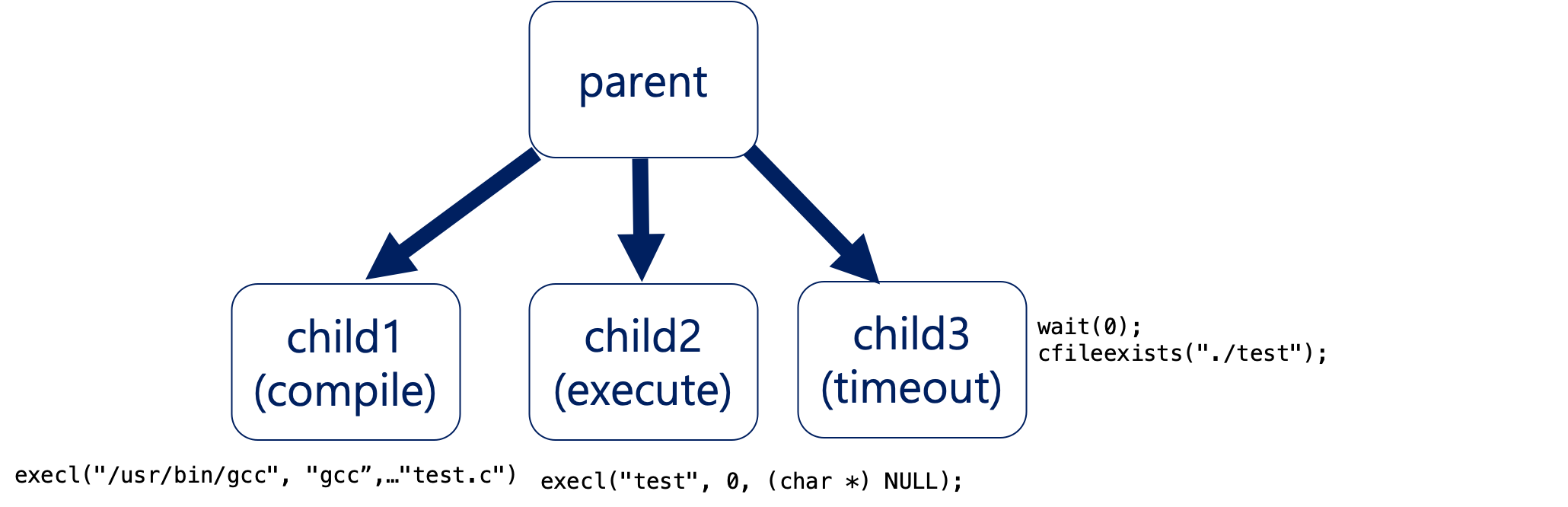
Fig 2. worker’s process family
3.5.1 How to compile and check
To compile “gcc” command has to be executed. For this, I have used execl. When this function is called, a control is given to the execl process and the termination is made inside the process. Therefore, we have to create a child process to compile. As seen in figure 2, you create a child process. In child process, the parent process waits until the child1 process is over. If there is a compiled file named “test,” the compile succeeds, otherwise the parent process returns the build fail message.
3.5.2 How to execute the compiled file with stdin
As the file named “test” created, the execution with the stdin to create an output starts. To do so, the child process number 2 is created to run the execution. By using freopen, stdin, stdout and stderr file can be decided. All of them work as a real standard input. When the error is detected, it gives error message to the stderr file. If there is no error, then the stdout file will have the result. It returns the result back to the file.
freopen(“input.in”, “r”, stdin); freopen(“output.out”, “w”, stdout); freopen(“error.out”, “a+”, stderr); execl(“test”, 0, (char *) NULL); exit(0);
4. Issues to Discuss
4.1 The Issue of Multithreading and Data size
As it deals with multiple users, and worker has to work at least 10 times per user with different standard input, there has been a possibility of using multithreads. However, we failed to implement multithreading because the data we send to worker gets to big. Sometimes, the testcase input to send to worker is greater than 6 million bytes. We had trouble handling more than one input because of the size. To send multiple data to worker there should be a better way to handle enormously large input data. Moreover, if we can use ThreadPool, it seems to be able to save wasted for creating the process.
4.2 The issue of Pipe
As mentioned above, we used alarm signal to deal with a problem with a run time of more than or same as 3 seconds. Because the process that the alarm signal receives is terminated, we used fork() to create the child process and it handles alarm signal before terminated. Since the child process handles alarm signal, parent process cannot know whether run time exceeds 3 seconds or not. We need a data transfer between parent process and child process. We judged that the pipe was completely suitable to meet our needs. However, we suffered a series of endless debugging. We also saw many memory-related errors that we have never seen since we majored in computer science. It was meaningful, but we found an alternative plan. If we have a chance, I want to implement it using a pipe.
5. GuideLine for this program
5.1 Commands for this program
5.1.1 Submitter Command
./submitter -n
-
Ex. ./submitter -n 127.0.0.1:8090 -u 21500670 -k 12345678 submit.c
5.1.2 Instagrapd Command
./instagrapd -p
-
Ex. ./instagrapd -p 8090 -w 127.0.0.1:8091 ./testcase
5.1.3 Worker Command
./worker -p
Ex. ./worker -p 8091
5.2 How to Use Makefile
- make : you can make instagradp, submitter, worker objects
- make clean : clear everything.
InstaGraP을 마치며..
음… 뭐랄까 진짜 재밌게 할 수 있을거 같았는데 시간이 따라주지 않아서 제대로 끝마치지 못한 것 같아 너무 아쉽다.
그래도 짧은 시간동안 내가 할 수 있는 최선을 다했고 재밌었다. 이제 막 배운 Process, Thread, Signal, 프로세스간의 통신을 실제로 구현해보면서 참 많이 배웠다, OS를 완전 잘 공부했는지는 모르겠지만 물어보면 아 나 그거 해보긴 했어요! 라고 말할 수 있을 것 같다 ㅎㅎ 잘 가랏! 안녀엉~
Subscribe via RSS
