(백준 알고리즘 문제풀이) 1520번 내리막 길
by 줌코딩
문제
문제 접근
- 문제를 보고 디피로 어떻게 접근할까 하다가 그냥 나는 이 문제를 priority queue를 활용한 bfs로 접근하는 게 좋겠다고 판단했다.
- 아래와 같은 경우에 대해서는 뒤로 돌아가는 경우가 발생하는데 이를 해결하기 위해서는 해당 위치까지의 경우의 수를 모두 구한 후에 이를 다음으로 전달하는 것이 맞다고 생각했다.
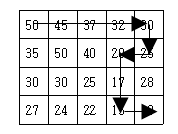
- 내리막길이 될 수 있는 친구를 맥스힙에 넣어주어 해당 계단까지의 경우의 수를 모두 구한 경우만 top으로 불러내어 연산을 진행한다.
코드
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pip pair<int, pii>
using namespace std;
int n, m, arr[501][501], ans[501][501], visited[501][501], d[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)arr[i][j] = readInt();
}
priority_queue<pip, vector<pip>, less<pip> > pq;
pq.push(pip(arr[0][0], pii(0, 0)));
ans[0][0] = 1;
visited[0][0] = 1;
while(!pq.empty()){
pip top = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int tv = top.first, tx = top.second.first, ty = top.second.second;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = tx + d[i][0], ny = ty + d[i][1];
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m)continue;
if(arr[nx][ny] < tv) {
ans[nx][ny] += ans[tx][ty];
if(!visited[nx][ny]){
visited[nx][ny] = 1;
pq.push(pip(arr[nx][ny], pii(nx, ny)));
}
}
}
}
printf("%d", ans[n-1][m-1]);
}
느낀점
- 이것도 결과 값을 저장해서 이용하므로 한켠으로는 디피라고 볼 수 있을 것 같다ㅎㅎ
이 포스팅은 쿠팡 파트너스 활동의 일환으로, 이에 따른 일정액의 수수료를 제공받습니다.
Subscribe via RSS
